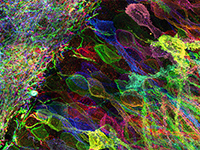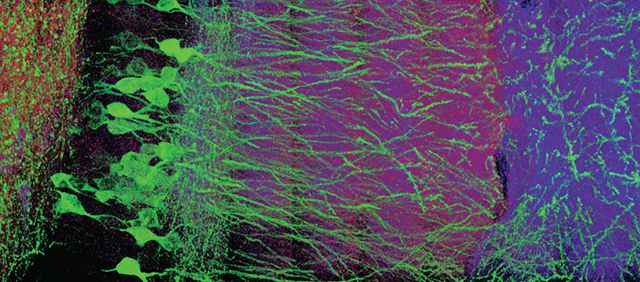
In optical microscopy, fine structural details are resolved by using refraction to magnify images of a specimen. We discovered that, by synthesizing a swellable polymer network within a specimen, it can be physically expanded, resulting in physical magnification. By covalently anchoring specific labels located within the specimen directly to the polymer network, labels spaced closer than the optical diffraction limit can be isotropically separated and optically resolved, a process we call expansion microscopy (ExM). Thus, this process can be used to perform scalable super-resolution microscopy with diffraction-limited microscopes. We demonstrate ExM with apparent ~70 nm lateral resolution in both cultured cells and brain tissue, performing three-color super-resolution imaging of ~10^7 µm^3 of the mouse hippocampus with a conventional confocal microscope.