Cell type–specific expression of optogenetic molecules allows temporally precise
manipulation of targeted neuronal activity. Here we present a toolbox of four
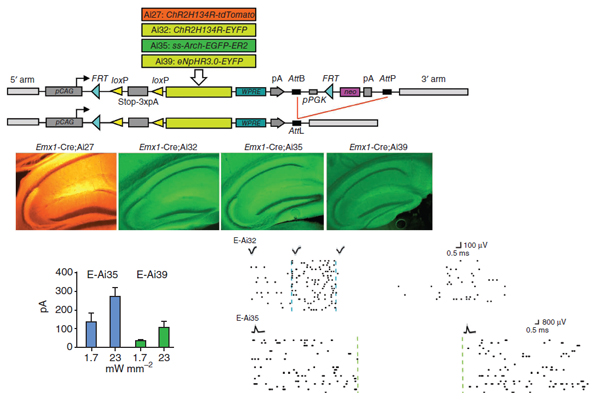
knock-in mouse lines engineered for strong, Cre-dependent expression of
channelrhodopsins ChR2-tdTomato and ChR2-EYFP, halorhodopsin eNpHR3.0 and
archaerhodopsin Arch-ER2. All four transgenes mediated Cre-dependent, robust
activation or silencing of cortical pyramidal neurons in vitro and in vivo upon
light stimulation, with ChR2-EYFP and Arch-ER2 demonstrating light sensitivity
approaching that of in utero or virally transduced neurons. We further show specific
photoactivation of parvalbumin-positive interneurons in behaving ChR2-EYFP reporter
mice. The robust, consistent and inducible nature of our ChR2 mice represents a
significant advance over previous lines, and the Arch-ER2 and eNpHR3.0 mice are to
our knowledge the first demonstration of successful conditional transgenic
optogenetic silencing. When combined with the hundreds of available Cre driver
lines, this optimized toolbox of reporter mice will enable widespread investigations
of neural circuit function with unprecedented reliability and accuracy.