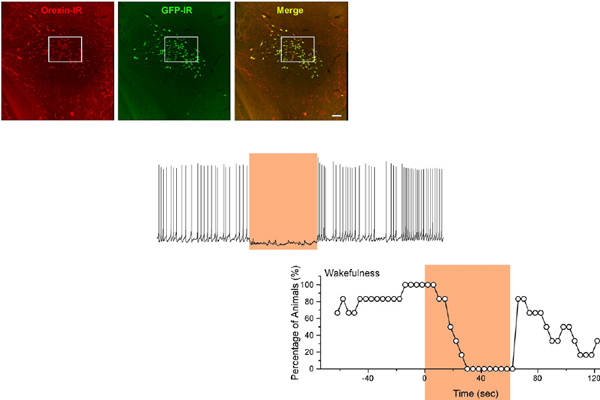
Orexin/hypocretin neurons have a crucial role in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. To help determine how these neurons promote wakefulness, we generated transgenic mice in which orexin neurons expressed halorhodopsin (orexin/Halo mice), an orange light-activated neuronal silencer. Slice patch-clamp recordings of orexin neurons that expressed halorhodopsin demonstrated that orange light photic illumination immediately hyperpolarized membrane potential and inhibited orexin neuron discharge in proportion to illumination intensity. Acute silencing of orexin neurons in vivo during the day (the inactive period) induced synchronization of the electroencephalogram and a reduction in amplitude of the electromyogram that is characteristic of slow-wave sleep (SWS). In contrast, orexin neuron photoinhibition was ineffective during the night (active period). Acute photoinhibition of orexin neurons during the day in orexin/Halo mice also reduced discharge of neurons in an orexin terminal field, the dorsal raphe (DR) nucleus. However, serotonergic DR neurons exhibited normal discharge rates in mice lacking orexin neurons. Thus, although usually highly dependent on orexin neuronal activity, serotonergic DR neuronal activity can be regulated appropriately in the chronic absence of orexin input. Together, these results demonstrate that acute inhibition of orexin neurons results in time-of-day-dependent induction of SWS and in reduced firing rate of neurons in an efferent projection site thought to be involved in arousal state regulation. The results presented here advance our understanding of the role of orexin neurons in the regulation of sleep/wakefulness and may be relevant to the mechanisms that underlie symptom progression in narcolepsy.