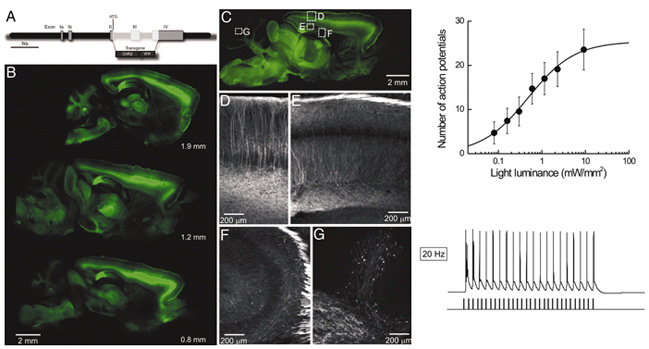
To permit rapid optical control of brain activity, we have engineered multiple lines of transgenic mice that express the light-activated cation channel Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) in subsets of neurons. Illumination of ChR2-positive neurons in brain slices produced photocurrents that generated action potentials within milliseconds and with precisely timed latencies. The number of light-evoked action potentials could be controlled by varying either the amplitude or duration of illumination. Furthermore, the frequency of light-evoked action potentials could be precisely controlled up to 30 Hz. Photostimulation also could evoke synaptic transmission between neurons, and, by scanning with a small laser light spot, we were able to map the spatial distribution of synaptic circuits connecting neurons within living cerebral cortex. We conclude that ChR2 is a genetically based photostimulation technology that permits analysis of neural circuits with high spatial and temporal resolution in transgenic mammals.